Why do we need Multilayer PCB?
The Advantages of Multilayer PCB
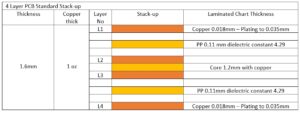
Having more layers means the board is thicker and, therefore, more durable than single-sided PCBs. This is another reason adding functionality through additional layers is preferable to increase the dimensions of a single layer. Printed circuit boards have ubiquitous presence today, what with them being the core of most electronic items. With the growing complexity of devices, Printed circuit boards are therefore increasingly becoming more complex. From flexible to odd shaped ones, there is a range of PCBS out there. While electronic devices with limited functions can do with single layer PCBs, there is an exponential growth in multi layered PCBs. By definition, multilayered PCB are made up of layers of double-sided circuit boards with heat protective insulation between them. The electrical connections between the layers happen through various kinds of vias resulting in complex multilayered PCBs. With complexity in applications, PCBs today can range anywhere from four to twelve layers.
- Size: Multilayer PCB have an added advantage on account of their small size as they lend themselves well.
- Lightweight: Small PCBs also come with reduced weight. This is particularly true also because single and double layered PCBs need a number of connectors that add to the weight and hence restrict mobility.
- Reliability: Typically multilayered PCBs are high on reliability as well as of high quality.
- Durability: Multilayer PCBs also come with high durability as they are able to withstand the heat and pressure that is applied on them.
- Flexibility: For assemblies that use flexible construction techniques, a flexible multilayered PCB can be helpful particularly in applications that require some amount of bending.
- Powerful: Multilayer PCBs typically are high density and have greater capacity as well as speed.
- Single Connection Point: With single connection points, multilayered PCBs are beneficial for gadgets where size and weight are constraints.
On account of all these advantages, multilayer PCBs are the preferred option especially as greater functionality and reduced size increasingly become the norm.
All of this is not to say that multilayered PCB Fabrication does not have any disadvantages. Largely, compared to single layered PCBs, multilayered ones come with added cost as well as increased design time. Multi layered PCBs also necessitate that there be skilled designers who have a wide experience and hence can overcome issues related to crosstalk and impedance. In efficient design it can directly impact board functioning. Also, multilayer boards require increased production time and hence a lower turnover rate.
However, it is their improved functionality that more than covers for the many disadvantages associated with multi layered boards. As far as their increased costs go, with the advancement of technology, the costs are only slated to decrease.
However, even while using multi layered PCBs it is important to ensure that as far as possible you go with an even number of layers as opposed to PCBs with odd number of layers. This is on account of many factors including but not limited to the cost efficiency:
Single layer PCBs are cost ineffective
The cost ineffectiveness of odd number of layers stems from the fact that the process of creating an odd layered PCB begins with creating an even layered PCB and then etching away the unwanted layer. As the process suggests, this leads to a lot of wastage which in turn lead to cost inefficiencies.
Warping
Other than the cost aspect, etching also results in warping of the layer. With one side having copper and the other side not having it, there are different cooling rates, thereby creating stress on the PCB.
Risk of over & under plating
What the etching also does is that it leaves the two sides (one with copper and one without), with different weights, thereby adding to the risk of under or over plating.
On account of all the above reasons, it isn’t advisable to have single layers unless there is a specific, compelling reason to do so.
Why do we need Multilayer PCB? Read More »